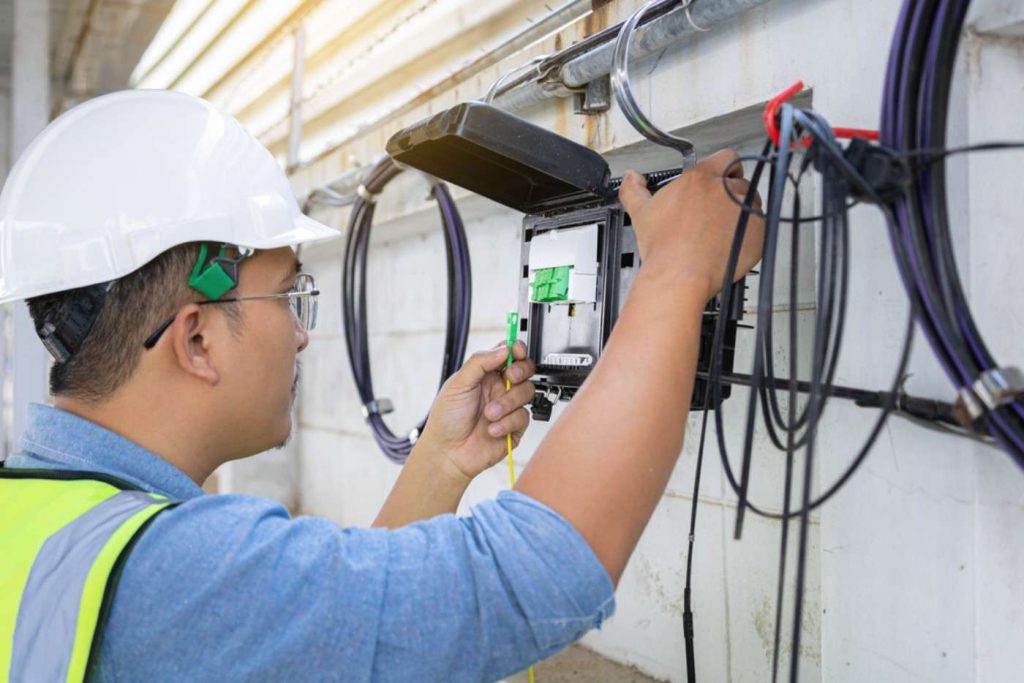
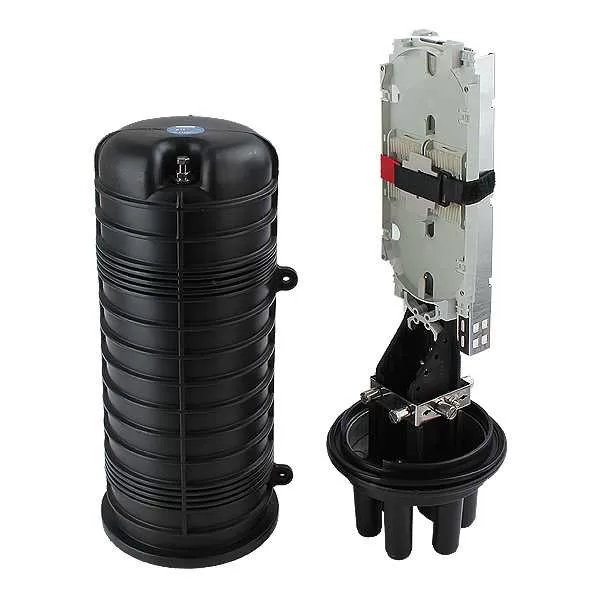
In the fast-paced world of telecommunications, data transmission has become a critical aspect of our daily lives. Fiber optic technology plays a crucial role in enabling high-speed and reliable data transfer.
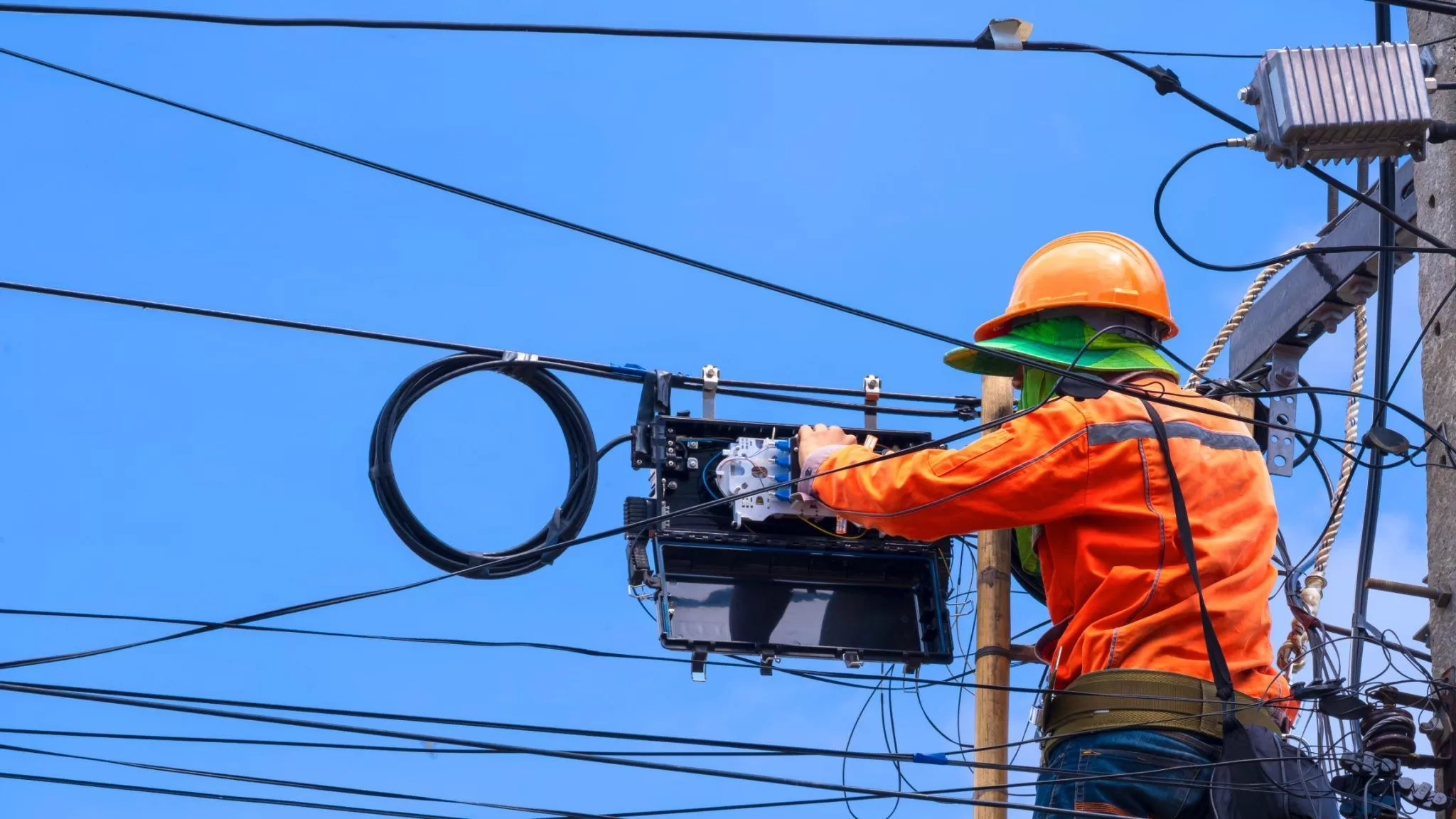

One key component of fiber optic networks is the fiber optic junction box. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the where, what, and how of fiber optic junction boxes, providing beginners with a solid understanding of their applications, types, inner structures, material considerations, and how to choose the right one for specific needs.
1. Introduction to Fiber Optic Junction Boxes
A fiber optic junction box, also known as a fiber optic distribution box or termination box, is a protective enclosure that facilitates the connection and management of fiber optic cables. It serves as a central point for organizing and distributing optical fibers, ensuring efficient connectivity and protection against environmental factors.
2. Where to Use Fiber Optic Junction Boxes
Fiber optic junction boxes find applications in various settings, including:
- Telecommunication Networks: They are used to connect and manage fiber optic cables in telecommunication networks, ensuring seamless communication.
- Data Centers: Fiber optic junction boxes play a crucial role in data centers, enabling the organization and distribution of high volumes of data with minimal signal loss.
- Residential Installations: In homes, these boxes are used to terminate and distribute fiber optic connections for internet and multimedia services.
- Industrial Environments: Industries use fiber optic junction boxes to create reliable and high-speed communication networks within manufacturing plants and other facilities.
3. Types of Fiber Optic Junction Boxes
There are several types of fiber optic junction boxes designed for specific applications. The main types include:
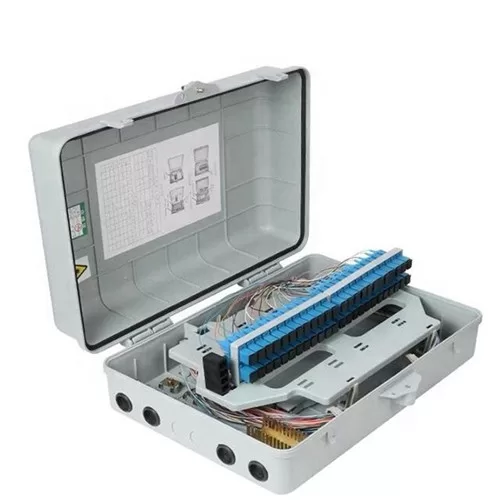

- Wall-Mounted Junction Boxes: Ideal for indoor applications, these boxes are mounted on walls and provide a neat and organized solution for fiber optic cable termination.
- Rack-Mounted Junction Boxes: Commonly used in data centers, these boxes can be mounted on standard equipment racks, allowing for efficient cable management and easy access.
- Outdoor Junction Boxes: Designed to withstand environmental elements, these boxes are weatherproof and suitable for outdoor installations.
- Dome Closure Boxes: Used for aerial and underground applications, these boxes are dome-shaped and provide protection against moisture and environmental contaminants.
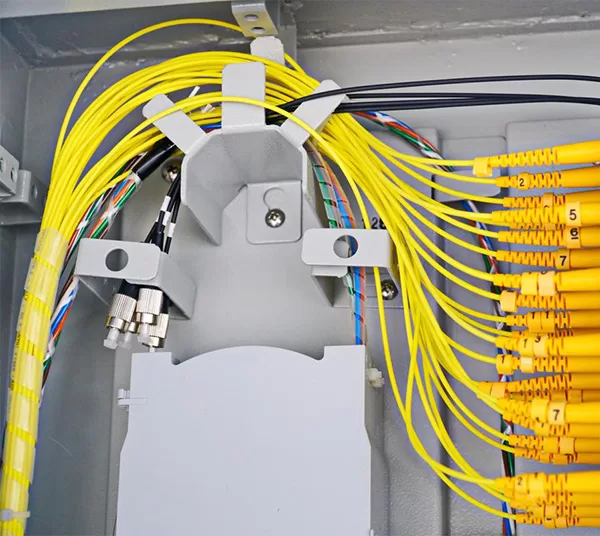
4. Inner Structure of Fiber Optic Junction Boxes
Understanding the inner structure of a fiber optic junction box is essential for proper installation and maintenance. The key components include:
- Splice Trays: These trays hold and protect the spliced fibers, ensuring a secure and organized arrangement.
- Cable Management: Features like cable entry and exit points, as well as spooling mechanisms, help in organizing and securing the incoming and outgoing fiber optic cables.
- Connectors and Adapters: Junction boxes have ports for connectors and adapters, allowing for easy and secure connection of fiber optic cables.
- Sealing and Protection: The inner structure is designed to protect the delicate fibers from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical damage.
5. How to Choose the Right Fiber Optic Junction Box
Selecting the appropriate junction box is crucial for the success of a fiber optic network. Consider the following factors when making a choice:
- Application: Choose a box that suits the specific application, whether it’s for indoor, outdoor, residential, or industrial use.
- Capacity: Ensure that the junction box has sufficient capacity to accommodate the number of fibers needed for your network.
- Protection Level: For outdoor installations, select a box with a high IP (Ingress Protection) rating to shield the fibers from environmental elements.
- Ease of Installation: Look for features that facilitate easy installation, such as multiple cable entry points and user-friendly cable management.
- Future Expansion: Opt for a junction box that allows for easy expansion or upgrades to accommodate future growth in your network.
6. Materials Used in Fiber Optic Junction Boxes
The materials used in the construction of fiber optic junction boxes contribute to their durability and performance. Common materials include:
- Metal: Metal junction boxes are robust and provide excellent protection against physical impact. They are suitable for industrial and outdoor environments.
- Plastic: Plastic boxes are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for indoor and residential applications where heavy-duty protection is not required.
- Weatherproof Materials: For outdoor installations, boxes made from weather-resistant materials, such as UV-resistant plastics or aluminum, are essential to ensure longevity.
7. Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for the optimal performance of fiber optic junction boxes. Here are some tips:
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, ensuring that cables are correctly spliced and secured.
- Seal Properly: In outdoor installations, pay special attention to sealing the box to prevent moisture ingress, which can lead to signal degradation.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections to check for any signs of damage, wear, or environmental factors that may affect the performance of the junction box.
- Labeling: Clearly label cables and connectors to simplify troubleshooting and future maintenance tasks.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, fiber optic junction boxes are indispensable components in modern communication networks. Whether you’re setting up a home internet connection or managing a large-scale data center, understanding the applications, types, inner structure, material considerations, and selection criteria for these boxes is essential. By following best practices in installation and maintenance, you can ensure a reliable and high-performance fiber optic network that meets your current needs and allows for future expansion.